The Tools to Persuade
Students use examples from the pro- and anti-suffrage movements to dissect the persuasive techniques used to shape public opinion then and now.
Get even more great free content!
This content contains copyrighted material that requires a free NewseumED account.
Registration is fast, easy, and comes with 100% free access to our vast collection of videos, artifacts, interactive content, and more.
NewseumED is provided as a free educational resource and contains copyrighted material. Registration is required for full access. Signing up is simple and free.
With a free NewseumED account, you can:
- Watch timely and informative videos
- Access expertly crafted lesson plans
- Download an array of classroom resources
- and much more!
- Current Events
- Journalism
- Women's Rights
- 7-12
(Note: For more support, see expanded procedure in downloadable lesson plan.)
- In advance, review the example worksheet at the end of the lesson plan packet. You may wish to distribute it to your students, as well.
- Students review tools of persuasion, then chart which of those tools are used in an artifact chosen from NewseumED’s women’s suffrage media map (below).
- Students discuss the effects of these techniques on the women’s suffrage debate.
- Students discuss what persuasive techniques are used in today’s media and how, and compare and contrast them with examples of persuasive materials from the suffrage debate.
- Persuasion Techniques worksheet (download), one per student
- Internet access. Share the link to the women's suffrage media map with your students, or project it on the board.
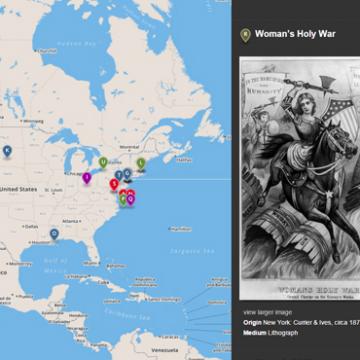
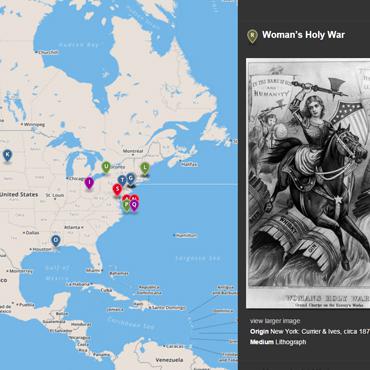
Women's Suffrage Movement Media Map
Women's Suffrage Movement Media Map
Have students present their findings. Prompts include:
- How do today’s persuasive messages look the same as those from the suffrage debate? How are they different?How do you explain the similarities and differences?
- Look at a specific technique. How are the ways that the pro- or anti-suffrage authors used this technique the same and different from the ways that the modern-day examples use the technique? How do you explain the similarities and differences?
- What additional persuasive techniques do the modern-day media have available to them due to technological developments?
- Why is it important to understand the tools and influence of persuasive messages? What impact do they have on our lives today?
-
Common Core State Standards: CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.CCRA.R.1
Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. -
Common Core State Standards: CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.CCRA.R.2
Determine central ideas or themes of a text and analyze their development; summarize the key supporting details and ideas. -
Common Core State Standards: CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.CCRA.R.3
Analyze how and why individuals, events, or ideas develop and interact over the course of a text. -
Common Core State Standards: CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.CCRA.SL.1
Prepare for and participate effectively in a range of conversations and collaborations with diverse partners, building on others' ideas and expressing their own clearly and persuasively. -
Common Core State Standards: CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.CCRA.SL.3
Evaluate a speaker's point of view, reasoning, and use of evidence and rhetoric.
-
National Center for History in the Schools: NCHS.Historical Thinking.3
A. Compare and contrast differing sets of ideas. B. Consider multiple perspectives. C. Analyze cause-and-effect relationships and multiple causation, including the importance of the individual, the influence of ideas. D. Draw comparisons across eras and regions in order to define enduring issues. E. Distinguish between unsupported expressions of opinion and informed hypotheses grounded in historical evidence. F. Compare competing historical narratives. G. Challenge arguments of historical inevitability. H. Hold interpretations of history as tentative. I. Evaluate major debates among historians. J. Hypothesize the influence of the past.
-
National Council of Teachers of English: NCTE.3
Students apply a wide range of strategies to comprehend, interpret, evaluate, and appreciate texts. They draw on their prior experience, their interactions with other readers and writers, their knowledge of word meaning and of other texts, their word identification strategies, and their understanding of textual features (e.g., sound-letter correspondence, sentence structure, context, graphics).
-
Center for Civic Education: CCE.V
A. What is citizenship? B. What are the rights of citizens? C. What are the responsibilities of citizens? D. What civic dispositions or traits of private and public character are important to the preservation and improvement of American constitutional democracy? E. How can citizens take part in civic life?
-
NCSS Curriculum Standards: NCSS 1
Learners will understand how human beings create, learn, share and adapt to culture. -
NCSS Curriculum Standards: NCSS 2
Learners examine the institutions, values and beliefs of people in the past, acquire skills in historical inquiry and interpretation, and gain an understanding of how important historical events and developments have shaped the modern world. -
NCSS Curriculum Standards: NCSS 5
Students know how institutions are formed, maintained and changed, and understand how they influence individuals, groups and other institutions. -
NCSS Curriculum Standards: NCSS 6
Learners will develop an understanding of the principles, processes, structures and institutions of government, and examine how power and authority are or have been obtained in various systems of government. -
NCSS Curriculum Standards: NCSS 10
Learning how to apply civic ideals to inform civic action is essential to participation in a democracy and support for the common good.